Disregard the Java hate wagon
Java is often hated for various reasons one of them is being too verbose.

However it's a great language that's continuously evolving and it's an absolute king of enterprise software, for the good or the bad. One of its main strengths is the Spring Framework, and for anyone who wants to make a project quickly Spring Boot is the fastest and easiest way to make your backend with Java. Spring is a tested framework that has evolved through the years, just like Java, it's secure and you can find any bugs you will encounter on StackOverflow with ease.
Under the hood Spring is very complex and let's you trivialize a lot of needed implementations thanks to its inversion of control and dependency injection, you use all the power of the framework through annotations.
Start the project
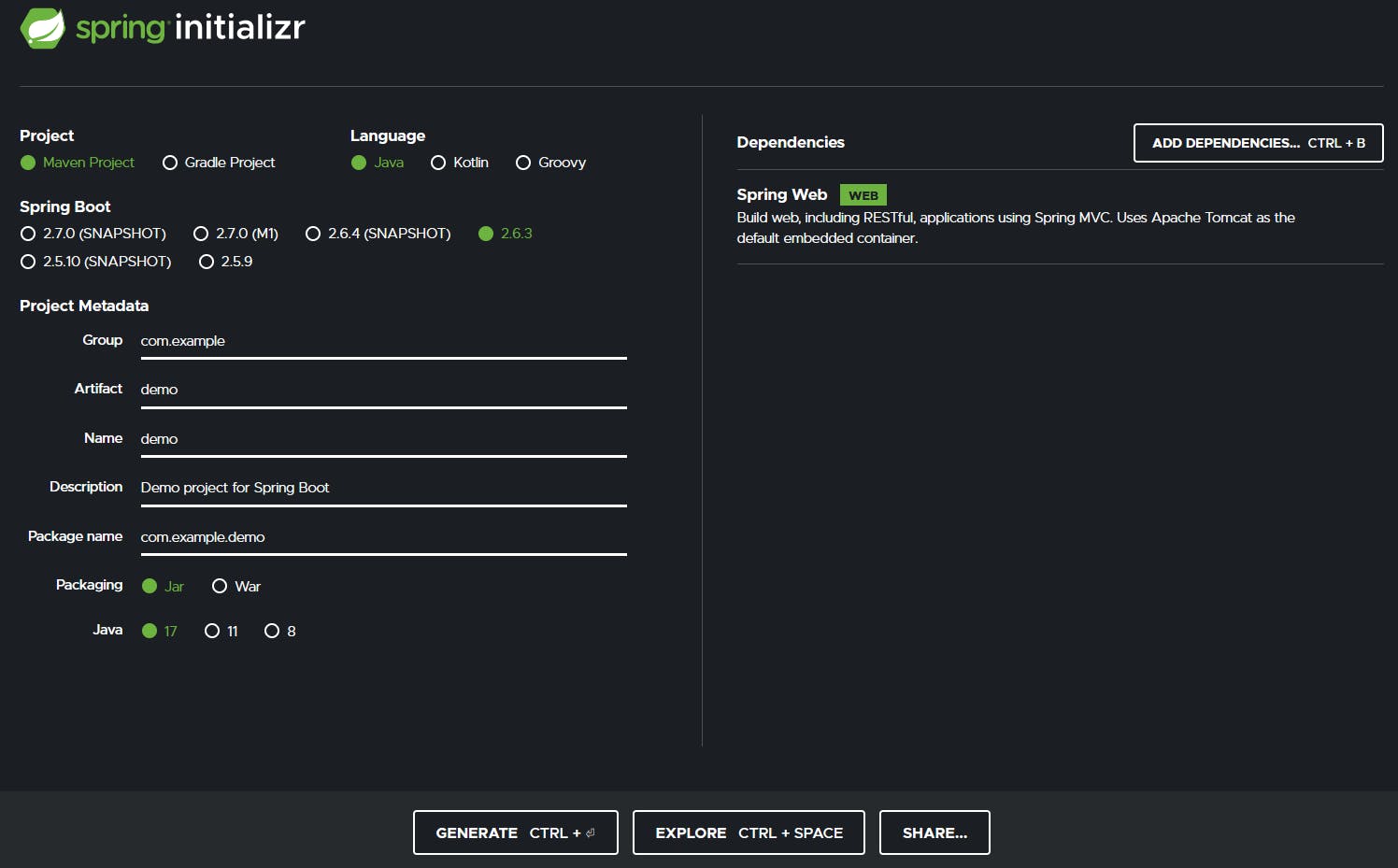
Start the project with Spring Initializr if your IDE doesn't have it built-in just download it (generate) from the site and include the dependency of Spring Web as follows:
RestController
After you have started your project all you need to do is make a new class anywhere and just add the @RestController this will instantly tell Sping that this class will have RESTful endpoints:
@RestController
public class Controller {
}
RestController annotation will make this class the controller meaning that it's listening to htttp://localhost:8080 calls and replying with whatever endpoints you have made.
For clarification:
- 8080 is the default port but you can change it in
application.properties - all the Spring annotations start with @
GetMapping
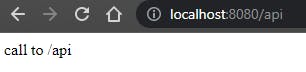
This GetMapping annotation makes the htttp://localhost:8080/api endpoint, after the call it will return or do whatever you put in the api() method. The name of the method is irrelevant, and it can also be void.
If you want your endpoint to be something other than /api just write the name you want.
@GetMapping("/api")
public String api(){
return "call to /api";
}
When you type in the browser the URL you will see the following:
RequestParam
If you want to extract a query parameter in your get method then you need to add the RequestParam as the following:
@GetMapping("/call")
public String call(@RequestParam(value = "val") String val){
return "the val is "+val;
}
This is an example of a call:
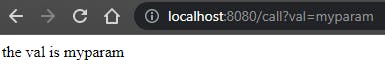
The enpoint htttp://localhost:8080/call will read the parameter you pass in the browser, for example
http://localhost:8080/call?val=myparam
Controller class code & TL;DR
//@RestController annotation will make this class the controller
//meaning that it's listening to htttp://localhost:8080 calls
//and replying with whatever endpoints you have made
@RestController
public class Controller {
//@GetMapping annotation makes the htttp://localhost:8080/api endpoint
//it will return or do whatever you put in the api() method
@GetMapping("/api")
public String api(){
return "call to /api";
}
//the enpoint is htttp://localhost:8080/call
//it also reads the parameters you pass in the browser
//for example http://localhost:8080/call?val=myvalue
//it can read the parameters because of the @RequestParam annotation
@GetMapping("/call")
public String call(@RequestParam(value = "val") String val){
return "the val is "+val;
}
}
Official Spring documentation: